Supply Chain Compliance
Supply chain compliance refers to policies and procedures to ensure that a company’s suppliers and vendors are not subject to sanctions, export controls or other restrictions imposed by national laws. Violations of relevant restrictions can occur at any point in the supply chain, including the sourcing of raw materials, production, transportation or distribution of goods.
Examples of supply chain compliance violations that may result in penalties include:
Forced labor: Using forced or slave labor in the supply chain.
Sanctions: Doing business with companies or individuals, or using vessels and aircraft, that are subject to government or international sanctions lists such as US OFAC SDN sanctions, EU Sanctions, or UN Sanctions.
Export controls: Importing, exporting, or re-exporting goods to prohibited countries like Iran, Russia and China. This includes facilitating transfers to restricted parties identified by authorities such as the US Bureau of Industry and Security lists or Japan METI end-user lists.
Law Enforcement: Doing business with persons wanted by the US FBI, Europol, Interpol and other law enforcement agencies.
Fraud, Bribery and Corruption: Engaging in business with companies and individuals who are involved in fraud and debarred from contracts, or not putting appropriate measures in place when engaging with politically exposed persons (PEPs) who are at higher risk of money laundering or corruption.
Environmental damage: Companies may be held accountable for illegal dumping, hazardous waste production and deforestation in their supply chain.
Reputational Risk: Utilizing vendors and suppliers that are facing severe and public scrutiny can lead to government investigations, financial losses and follow-on scrutiny.
High Risk Ownership: Having counterparties owned by individuals or entities that have forced labor, sanctions, bribery or other types of risk.
Start complying today
What Happens If A Company Has No Supply Chain Compliance?
Penalties generally start at seizure and forfeiture of articles and revocation of exporting privileges, and can go all the way up to $1,000,000 per violation, and ten years of imprisonment for executives in charge of supply chain and risk. Senior executives can also be personally held liable for fines and be banned from their industry for a prolonged period of time, or permanently.
These regulations apply fully or partially, in the United States, UK, EU and dozens of other countries, and even where laws do not explicitly forbid doing business with internationally sanctioned parties, or using slave labor, the damage to reputations can be significant.
Notable supply chain fines and penalties include:
U.S. Customs and Border Protection officials have blocked more than 2,300 shipments from entering the U.S. due to forced labor-linked goods from China’s Xinjiang region. January alone saw 282 shipments stopped over forced labor concerns, according to Customs.
US Customs seized aluminum in January 2023 which was produced in Xinjiang using forced labor.
Goods from Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, and those of other China-based companies have been confiscated at US ports for forced-labor violations as recently as December 2022.
The US Department of Justice in December 2022 issued an indictment against individuals involved in illegally exporting controlled items to Russia.
Elf Cosmetics was penalized almost $1 million for sanctions violations involving North Korean-made fake eyelashes in 2019.
The US government has publicly promised “Bigger Fines, Stepped Up Enforcement of Sensitive Technology Restrictions” and Germany recently enacted its “Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (LkSG).” The new German law entered into force 1 January 2023 and requires thousands of German companies to undertake extensive due diligence regarding the prevention of and response to human rights violations and environmental pollution in the supply chain, including monitoring, documentation and adaptation of these preventive and remedial measures on a case-by-case basis.
It is a very dangerous time to not have an active supply chain compliance program.
How To Comply Effectively
To avoid potential sanctions and maintain a good reputation, it is important for companies to establish robust supply chain compliance programs. The first step in any supply chain compliance program is to have a complete list of suppliers and vendors that is screened daily against global risk data.
This means ensuring that you have the legal names and addresses of your suppliers and vendors, their beneficial owners and any key individuals, as well as vessels and aircraft used to transport your goods. Then, screening this information daily against:
Sanctions lists
Export control lists
Contract debarment lists
Lists of politicians at high risk of bribery (Politically Exposed Persons)
Law Enforcement most wanted
Adverse Media
When screening suppliers and vendors, it is important to review alerts on a daily basis, and maintain a secure, standardized audit trail that can be shown to regulators. Since the status of a company or individual in the supply chain can change at any point, it is crucial to show regulators that compliance screening is regularly updated.
Additional methods that support screening can include measures such as supplier audits, training for employees and suppliers, and the development of codes of conduct and policies. Companies may also seek certification from third-party organizations to demonstrate their commitment to supply chain compliance.
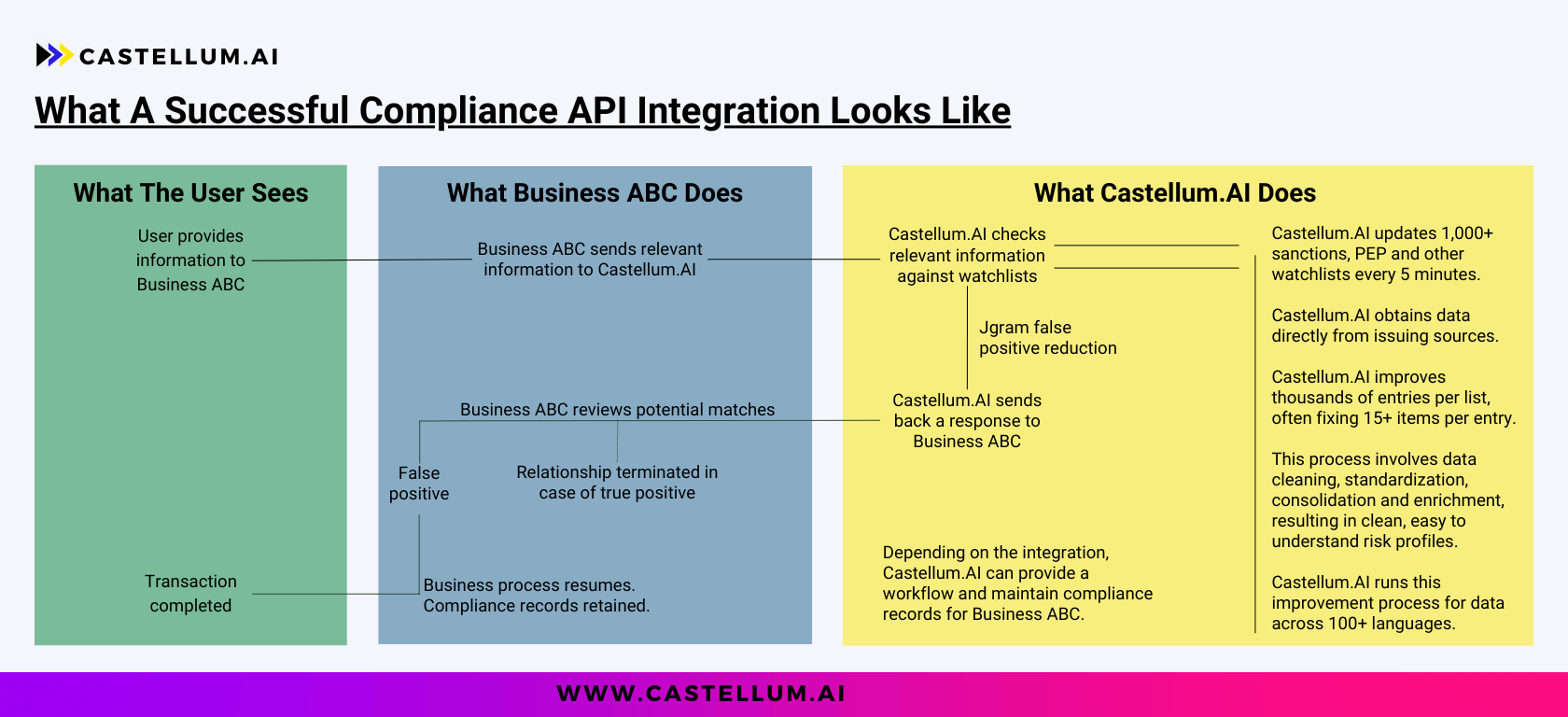
How to Integrate with Castellum.AI
Clients can either use our self-serve online platform, or our API. The platform is most effective for businesses that have fewer than 1,000 clients and fewer than 5,000 transactions annually. For anything higher volume, we recommend the API because it allows the most flexibility in terms of speed, scale and alert management.
Contact us to:
Upgrade your existing supply chain compliance process
Increase your supply chain risk coverage
Automate your supply chain compliance
Reduce your supply chain compliance false positives and workload
Automate Your Supply Chain Compliance
About Castellum.AI
Castellum.AI obtains global sanctions information from primary sources using a patented process to extract, standardize, clean and enrich the data, extracting key information like IDs and addresses from unstructured data. Castellum.AI enriches as many as fifteen separate items per entry. Castellum.AI’s database consists of over 1,000 watchlists covering over 200 countries and eight different categories (sanctions, export control, law enforcement most wanted, contract debarment, politically exposed persons, regulatory enforcement, delisted, and elevated risk). Castellum.AI checks for watchlist updates every five minutes directly from issuing authorities.