Ransomware Response and Sanctions Compliance
Global sanctions authorities have targeted cryptocurrency addresses over the past several years, including for ransomware-related reasons. The total number of sanctioned crypto addresses has more than doubled since the beginning of 2022. For example, in September 2022, the US sanctioned Iranian government-linked hackers and their crypto addresses for their involvement in ransomware attacks. Individuals associated with the REvil ransomware group have also been designated, as have crypto exchanges and other companies involved in laundering ransomware proceeds such as Garantex and Tornado Cash.
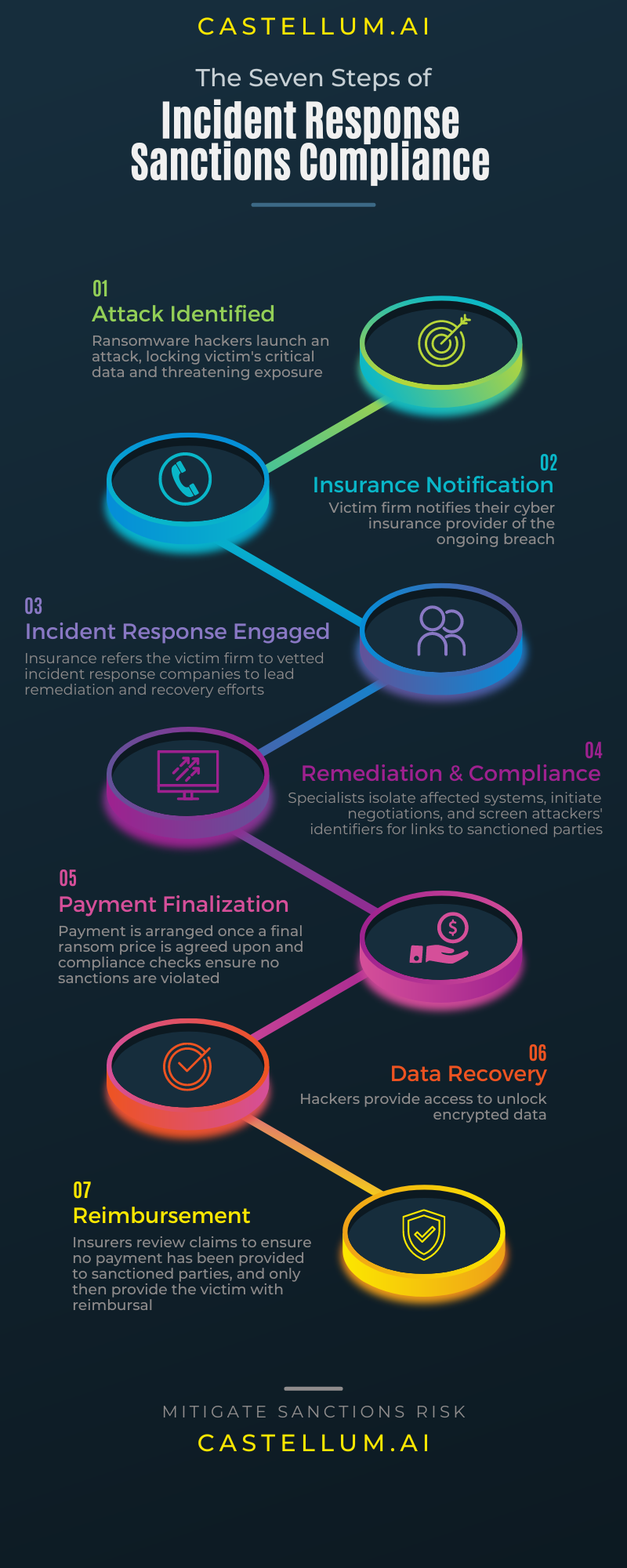
As a result, ransom payments carry a clear sanctions risk, and the US government has issued guidance requiring all parties involved in or facilitating a ransomware payment to comply with sanctions. Where does compliance sit within the ransomware response lifecycle? We’ve broken down the process into 7 distinct stages and highlighted when sanctions should be screened.
1.Attack Identified
Ransomware attackers access a victim’s network and encrypt data or lock access to systems with personal identification information, business secret information, financial information, or other business critical data. The attackers may overtly declare the hack to the victim, or network monitoring systems may alert the victim to the ongoing intrusion.
2. Insurance Notification
Companies holding cyber insurance policies contact their insurance policy issuer to notify them of the ongoing attack. The cyber insurance company will most often provide the victim company with a list of approved incident response vendors to contact and initiate remediation efforts.
3. Incident Response Engaged
The victim company engages an incident response firm to lead the response. Factors that influence the vendor selection include whether the incident response firm has internal negotiation capabilities to engage with attackers if a breach cannot be remediated through means other than paying the ransom.
4. Remediation and Compliance
Incident response firms will assess the extent of the breach, assist the client in isolating affected systems, and ensure the hack does not spread. If commercially available tools to unlock the attacked systems are unavailable or if the victim assesses the damage of ransomed data being leaked is too great, the incident response company will initiate negotiations with the attackers.
Throughout this process, the incident response firm should be collecting information on the attackers, including but not limited to: crypto wallets where the attackers say they will receive a ransom, IP addresses, emails or other usernames, domains, and other identifying data. Identifying information like crypto addresses should be passed through a sanctions screening platform to ensure a payment is not directed to sanctioned parties.
5. Payment Finalization
Once a final ransom amount is agreed upon, the incident response firm will facilitate a payment. This may involve the client setting up a crypto wallet and purchasing the requisite cryptocurrency themselves, it may be organized by the incident response firm directly, or facilitated through a crypto liquidity provider – these are cryptocurrency brokers who assist with purchasing cryptocurrencies on behalf of victims. Before any exchange of funds, all parties involved in the transaction are obligated to screen the attackers’ available information to ensure payments are not directed to sanctioned parties. Critical to this process is generating permanent audit records to prove that sanctions were screened.
6. Data Recovery
Following a ransom payment, victims receive a key to unlock their affected data. The incident response provider works with the victim company to restore impacted systems and ensure that no backdoor is present for attackers to reinfect the victim’s systems.
7. Reimbursement
With the ransom successfully paid and the victim firm having restored its operations, an insurance claim is filed. The cyber insurance issuer will require documentation to prove that the ransom was not directed to sanctioned parties before a claim is resolved. Only then will the victim firm be reimbursed for losses, including the costs arising from the ransom payment and the incident response firm’s remediation efforts.
Screen crypto data and mitigate sanctions risk
About Castellum.AI
Castellum.AI automates compliance screening by providing watchlist screening solutions across an online platform, API, and bulk data.
Castellum.AI obtains global sanctions information directly from authorities issuing sanctions, and then proceeds to standardize, clean and enrich the data, extracting key information like IDs and addresses from text blobs. Castellum.AI enriches as many as fifteen separate items per entry.
The database consists of over 1,000 watchlists, covering over 200 countries and eight different categories (sanctions, export control, law enforcement most wanted, contract debarment, politically exposed persons, regulatory enforcement, delisted, and elevated risk). Castellum.AI checks for watchlist updates every five minutes directly from issuing authorities.